•
Via What’s Left
By Stephen Gowans
In a previous article I pointed to three factors to explain the West’s decision to intervene militarily in Libya to prevent the government there from putting down an armed rebellion while it tacitly approves the Gulf Cooperation Council’s military intervention in Bahrain to put down a peaceful rebellion there. The double-standard, I argued, reflects dramatic differences between Libya and Bahrain in their relationship with the United States and its dominant investor and corporate class.
Bahrain is the home of the US Fifth Fleet, has long-standing warm relations with Washington, and strongly caters to western corporate and investor interests. Since the Khalifa regime supports US corporate profit-making and military interests, and a new regime might not do the same to the same degree, Washington is prepared to allow Saudi and other GCC troops and tanks to assist Bahraini authorities in violently quelling a peaceful rebellion.
Libya, I pointed out, doesn’t provide bases for the US or other western militaries, hasn’t had long-standing warm relations with Washington, and isn’t particularly accommodating of western corporate and investor interests. From a neo-colonialist standpoint, western powers could do better in Libya.
Some readers objected, arguing that in recent years Libya has sought to open itself to western corporations and investors and has struck a number of deals with western oil companies. It cannot be concluded, they continued, that the West’s decision to intervene military in Libya was motivated by western profit-making considerations, for Libya is already catering to western business interests.
To be sure, Libya has opened itself to the West, but doing deals with western corporations is not the same as engineering a wholesale subordination of domestic interests to those of foreign bankers and corporations — typically, what corporate-and investor-oriented western governments look for in third-world ‘partners’. For the wealthy scouring the globe for investment opportunities and corporations seeking export markets, an opening door in Libya doesn’t necessarily mean that Libya’s business climate is fully conducive to maximising profits.
That Libya allows some western corporations to operate in the country doesn’t guarantee that investments are safe from expropriation, that performance requirements aren’t imposed on foreign investments, that repatriation of profits isn’t controlled, that taxes aren’t high, or that there is a commitment to labor market ‘flexibility’. In short, the Gaddafi government may, in recent years, have sought to expand western access to investment opportunities in Libya, but that alone doesn’t mean that the conditions of access were regarded by corporations and investors as being as desirable as they could be, or as desirable, for example, as those provided by the government of Bahrain, or a desirable as those a future government might provide.
The Heritage Foundation provides a guide to how accommodating countries are to the profit-making interests of US corporations and investors. Every year the foundation publishes an Index of Economic Freedom, which ranks countries on how open they are to exports and foreign investment, how low their taxes are, how committed they are to protecting property rights, and so on; in short, how strongly a country favors foreign businesses and investors over its own people.
Significantly, governments that are perennially targets of US government regime change efforts rank at or near the bottom of the index. This year’s list identifies the following 10 countries as the least economically free (ie, least accommodating to foreign businesses), in order, from worst to slightly better:
- North Korea
- Zimbabwe
- Cuba
- Eritrea
- Venezuela
- Myanmar
- Libya
- Democratic Republic of Congo
- Iran
- Timor-Leste
Seven of the bottom 10 (North Korea, Zimbabwe, Cuba, Venezuela, Myanmar, Libya and Iran) are the targets of open regime change operations by the United States and its allies, carried out ostensibly because the targeted countries are not protecting human rights, threaten regional stability, or in the case of Libya, because the government is said to be attacking its own people.
That these countries happen to be considered the least accommodating of foreign business profit-making points to an ulterior motive on the part of western governments to bring about regime change, and to use human-rights and humanitarian rhetoric as a cover for pursuing the economic interests of western corporate and investor elites.
Significantly, not one country in the top 10 is a target of western regime change efforts. If regime change were linked to human-rights concerns and not unfavorable investment and export conditions, we might expect to find regime change targets scattered throughout the rankings, rather than bunched up at the bottom.
One counter-explanation is that economically free countries tend to respect human rights, which is why the worst offenders on both counts are found at the bottom of the list. However, this couldn’t possibly be true, for the United States, which has an atrocious human rights record (Guantanamo, Abu Ghraib, torture and rendition of prisoners, arrest and detention without charge, extrajudicial assassination, weakening of Miranda rights, spying on its own citizens, restrictions on travel to Cuba, and so on) ranks as the ninth freest country in the world in economic terms, and Saudi Arabia, the least free country in terms of political and civil liberties and perhaps the most contemptuous of human rights, ranks in the top half.
Bahrain, as it turns out, is ranked number 10 of 179 countries on the Heritage Foundation list, next to the United States. Regionally, Bahrain is top ranked in North Africa and West Asia, while Libya, ranked 173 over all countries, falls dead last in regional rankings.
Bahrain’s higher ranking is based on an array of government policies aimed to please foreign businesses. Property ownership is secure and expropriation is unlikely, whereas in Libya foreign companies are vulnerable to expropriation. Bahrain welcomes foreign investment and allows new businesses to be 100 percent foreign owned and controlled, while Libya screens foreign investment, imposes performance requirements on foreign investors that domestic investors are not required to meet, and demands that Libyans have a 35 percent stake in foreign companies that operate in the country. And while Bahrain imposes no restrictions on repatriation of profits, Libya does.
On trade, Bahrain imposes few restrictions on imports, while Libya maintains a variety of tariff and non-tariff barriers to help local firms develop. With the exception of oil companies, businesses that operate in Bahrain pay no corporate tax, while businesses in Libya are subject to a tax rate as high as 40 percent. Personal income tax is extremely low in Bahrain, but can reach as high as 90 percent in Libya. And while Bahrain provides businesses maximum flexibility in dealing with employees, even allowing them to pay desperation-level wages, Libya demands that businesses meet minimum standards on pay and working conditions.
In short, the Bahraini monarchy runs a foreign-investment- and import-friendly regime, while Libya’s economic policies favour local investors and businesses and provide a minimal standard of protection for labor. A government that was more like Bahrain’s, and less like Gaddafi’s, would unquestionably be congenial to foreign business interests.
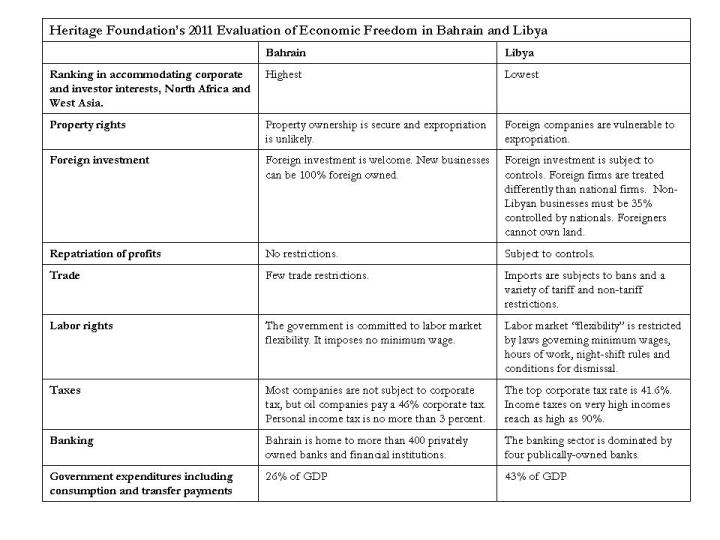
Heritage Foundation's 2011 evaluation of economic freedom in Bahrain and Libya
Some readers contend that western military intervention in Libya is aimed at preventing the slaughter of Libyan civilians. But a stronger case can be made that western military intervention is aimed at regime change, and that, far from protecting civilians, Nato bombing is only setting the stage for a prolonged civil war by weakening loyalist forces and thereby allowing the rebels to contest for power.
There are a number of reasons why the Nato operation in Libya can be seen as a regime change effort, apart from the motivation of replacing the current government with one more congenial to western profit-making interests, as discussed above.
First, the decision of the French government to recognise the rebel opposition as the legitimate government was a declaration that France, at least, is manoeuvring to install a new government in Libya. (1) Indeed, both France and Britain have acknowledged that they are seeking the ouster of Gaddafi. (2)
Second, US secretary of state Hilary Clinton said “Gaddafi’s ouster was the ultimate goal of the UN resolution” (3), and while US president Barack Obama denied this, he did say that the military “campaign will likely continue as long as Libyan leader Moammar Gaddafi is in power”. (4) If the intervention’s goal is to protect civilians and not install a new government, how can the aims of France and Britain and the comments of Clinton and Obama be reconciled?
Third, Washington hopes that sanctions “combined with Nato air power, will be enough to turn the tide militarily”. While the UN Security Council resolution authorises the use of military means to protect civilians, it doesn’t authorise the use of military means to aid rebel forces. Yet newspapers on 23 March 2011 were full of stories on how fresh airstrikes were allowing rebel forces to recover lost ground. For example, the Wall Street Journal commented that,
“The hope for the West is that a continuation of military pressure on Col Gaddafi’s forces, even at somewhat lower levels in coming days, combined with continued forward movement by the rebels, will be enough to make the Libyan army either buckle or turn on the Libyan leader. That would produce the outcome the West hopes for – the removal of Col Gaddafi.” (5)
Meanwhile, the New York Times reported that “the airstrikes have lifted the rebels back from the brink of defeat in the eastern city of Benghazi and enabled them to rush west along the coast past their farthest gains of the previous peak weeks ago”. (6)
It is clear that the intention of the military intervention, which was authorised when the rebels’ defeat by loyalist forces was imminent, was to weaken the government side to allow the rebels to rally and seize the momentum. This hardly favors a quick resolution of the conflict. The conflict could go on for some time, perhaps taking more lives than would have been lost had the UN sent a fact-finding mission in return for a cease-fire, or had loyalist forces successfully put down the uprising weeks ago.
The potential for the conflict to drag on, fuelled by the aid Nato provides the rebels through its airstrikes, was acknowledged by US secretary of defense Robert Gates. The Pentagon boss said “he couldn’t be sure Nato would have finished its mission by year-end”. (7)
The idea, then, that the UN Security Council authorised military intervention to protect civilians has no substance. Furthermore, the idea that the intervention is protecting civilians, whether that is the real intention of the intervention or not, seems unlikely, since the outcome so far has been to create the conditions for a protracted civil war – one moreover, that will be worsened by civilian deaths caused by Nato bombing on behalf of rebel forces.
If the rebel forces prevail and extend their control to all of Libya, or eventually settle for partition of the country, we can expect the economic policies of the future government to be closer to those of Bahrain, and therefore closer to the profit-making interests of western corporations and investors. In this sense, the UN Security Council, and the military operation it authorises, can be seen as investments in making Libya a more attractive place to do business in.
Finally, it might be pointed out, as Johnstone has, (8) that the Gaddafi government has invested a considerable part of its oil revenues in sub-Saharan Africa, contrary to the usual practice among Arab oil states of shipping the proceeds of their oil sales to New York investment banks, the London stock exchange, and US arms manufacturers. These practices are more conducive to western business interests than Gaddafi’s investments in Africa, and might be expected to become the standard practice in Libya if the rebel movement succeeds in ousting Gaddafi.
NOTES
1. ‘Why are they making war on Libya?’ by Diana Johnstone, Counterpunch, 24 March 2011
2. ‘Obama bets on limited engagement’ by Jay Solomon and Carol E Lee, Wall Street Journal, 24 March 2011
3. ‘Allies rally against Gadhafi’ by Keith Johnson, Yaroslav Trofimov and Sam Dagher, Wall Street Journal, 19 March 2011
4. ‘Allies strain to mend split’ by Nathan Hodge, Sam Dagher, Stephen Fidler and Stacy Meichtry, Wall Street Journal, 23 March 2011
5. ‘Fresh airstrikes aid rebels’ by Sam Dagher and Stephen Fiddler, Wall Street Journal, 28 March 2011
6. ‘Libyan rebels march toward Qaddafi stronghold’ by David D Kirkpatrick and Kareem Fahim, New York Times, 27 March 2011
7. ‘Fresh airstrikes aid rebels’ by Sam Dagher and Stephen Fiddler, Wall Street Journal, 28 March 2011
8. ‘Why are they making war on Libya?’ by Diana Johnstone, Counterpunch, 24 March 2011
•

The following statement was issued by Dave Roberts of the SLP.
As the West gears up for intervention into Libya, the left in Britain, with a few exceptions, are like rabbits in the proverbial headlights, transfixed by the brilliant glare of western propaganda. Many are either completely ignorant of Gaddafi’s anti-imperialist revolutionary history or prefer that their self-opinionated pseudo-left intellectualism should not be disturbed by the very notion that the people of one of the previously poorest and most backward countries in the world, through their own efforts, can have thrown off imperialism.
Not only that but, within four decades, they have gone on to built an economy and a society which, to the horror of western reactionary circles, is the envy of the revolutionary class-conscious, downtrodden and poor of Africa and the Arab world.
If any had bothered to read even a basic historical text on Libya’s Green Revolution they would be amazed at its achievements, benefits of which include universal suffrage, free lifelong education for all up to post-graduate level, free medical and health care, a guaranteed home for every Libyan and the highest per capita income in the Arab and African world – a per capita income which is a real average income rather than one based on the massive disparities in wealth to be found in western economies.
Unlike their Arab brothers and sisters in Egypt, Tunisia, Saudi or Jordan, at the age of 16 all Libyans are entitled to join and attend their weekly held local people’s committee and participate practically week in week out in the framing and delivery of policies and the allocation of resources that affect their daily lives. No wonder that participation rates in the political process exceed anything the ‘democratic’ west can offer.
A point lost on the BBC’s Jeremy Bowen when he insisted that protesters were “thirsting for democracy”. Gaddafi correctly told him that he clearly knew nothing of the policy and practice of the authority of the people in Libya .
In setting off on the journey to bring Libya into the modern world, Gaddafi has been conciliatory to those elements in society who, for reasons of the privilege or power they had held over the people through the mosques or through their previous patronage by western oil companies, have continued to resist the struggle for democratic and economic development.
He guaranteed participation of the imams in the people’s committees and ensured that the previous comprador class was no worse off as the wealth, education and health of all Libyans was raised to the remarkable levels they enjoy today. It is clearly these restorationist elements who are forming the backbone of the opposition, eyeing a chance for themselves of a ‘better’ future under the local patronage of western oil companies, or of bringing Libya under the pan-islamist resistance and ‘rescuing’ it from what they fear as the westernising modernism and growing secularism of the Green revolution.
Unlike the opposition in Egypt or Tunisia, the Libyan opposition have raised the royalist emblem of the western oil company-imposed puppet King Idris, whilst increasingly calling for western imperialist intervention to secure their counter-revolution. It should therefore be glaringly obvious to all but the politically blind that the struggle in Libya is the complete opposite to the unfolding struggle across the rest of the Arab world.
An understanding that might explain why Hague sent the SAS and MI6 on a secret mission to start discussions to begin arming the opposition in Libya, whilst two weeks earlier Cameron was in Egypt gun running to the military junta.
No calls for western intervention in Tunisia, Saudi Arabia, Jordan or Egypt then? No calls for the Bahraini or Saudi royals to be referred to the War Crimes Tribunal for having invaded sovereign countries and killed unarmed civilians? Unlike most of the British left, British imperialism has a consistent class line: support the junta in Egypt to hold back generalised intifada and destroy the Libyan revolution. Why? Because it has embodied, to date, the best organised and most resilient resistance in the Arab and African world.
Which is why Gaddafi was referred to by Nelson Mandela as one of the “greatest freedom fighters of the century”. Why the first country Mandela visited upon his release from 27 years in an apartheid gaol was Libya, in order to thank Gaddafi for his consistent support for the ANC. Why he is supported by and has supported Cuba, the Sandinistas, Chavez, the Palestinian cause, the Irish national struggle, etc, etc.
It would be a disaster for western oil companies and imperialism generally if any of the Libyan lessons learnt in 40 years of anti-imperialist struggle began to infect the generalised Arab revolt. Which might explain why a country with a population the size of Wales, albeit with better health and wealth indices, is now facing the combined political muscle and potential military threat of the European Union, the United States etc.
It is clearly a bigger ideological than military threat. Particularly at this time, against the background of the continued worldwide economic collapse of capitalism, its drive towards generalised warmongering, and its scramble to secure oil supplies and arms deals.
That any of these truths should get in the way of western warmongering propaganda has led to an unprecedented campaign to put the frighteners on western middle-class intellectuals. For example, the enforced resignation of Sir Howard Davies at the London School of Economics for accepting a donation from Saif Gaddafi’s foundation after the university had awarded him a PhD.
There is hardly a university in the UK that has not taken money from the ‘Gaddafi regime’, but, as the Daily Telegraph pointed out, the real sin was not taking the money but engaging in academic dialogue with the Libyans on the practice of direct democracy in Libya. Saif Gaddafi had been asked to deliver the Ralph Miliband Lecture (the father of the Miliband brothers, who, according to the Daily Telegraph, was, like Gaddafi, seeking his own ‘third way’, which was neither Soviet socialism nor western capitalism).
It should be as clear as crystal who are the reactionaries and who are the anti-reactionaries; who are the imperialists and who are the anti-imperialists in this pivotal struggle.
Of course, all class-conscious, anti-imperialist and progressive movements should stand shoulder to shoulder with the unfolding Arab revolt, but they should also stand for the victory of the Libyan revolution against western counter-revolution; it’s one and the same struggle. Although one doubts that much of the British left will understand that.
———-
Dave Roberts has visited Libya numerous times over the last 15 years, leading European delegations, participating in international roundtable conferences in Tripoli and Benghazi, and facilitating British academics in studying the workings of Libyan direct democracy. He has toured the country extensively, meeting with students, academics, health workers, members of people’s committees and the Revolutionary Committees Movement.
•
Cuba categorically rejects any attempt whatsoever to take advantage of the tragic situation created in order to occupy Libya and control its oil
Statement by Cuba’s Minister of Foreign Affairs to the UN Human Rights Council, Geneva, 1 March 2011, via Granma
Mr President:
Humanity’s conscience is repulsed by the deaths of innocent people under any circumstances, anyplace. Cuba fully shares the worldwide concern for the loss of civilian lives in Libya and hopes that its people are able to reach a peaceful and sovereign solution to the civil war occurring there, with no foreign interference, and can guarantee the integrity of that nation.
Most certainly the Libyan people oppose any foreign military intervention, which would delay an agreement even further and cause thousands of deaths, displacement and enormous injury to the population.
Cuba categorically rejects any attempt whatsoever to take advantage of the tragic situation created in order to occupy Libya and control its oil.
It is noteworthy that the voracity for oil, not peace or the protection of Libyan lives, is the motivation inciting the political forces, primarily conservative, which today, in the United States and some European countries, are calling for a Nato military intervention in Libyan territory. Nor does it appear that objectivity, accuracy or a commitment to the truth are prevailing in part of the press, where reports are being used by media giants to fan the flames.
Given the magnitude of what is taking place in Libya and the Arab world, in the context of a global economic crisis, responsibility and a long-term vision should prevail on the part of governments in the developed countries. Although the goodwill of some could be exploited, it is clear that a military intervention would lead to a war with serious consequences for human lives, especially the millions of poor who comprise four fifths of humanity.
Despite the paucity of some facts and information, the reality is that the origins of the situation in North Africa and the Middle East are to be found within the crisis of the rapacious policy imposed by the United States and its Nato allies in the region. The price of food has tripled, water is scarce, the desert is growing, poverty is on the rise and with it, repugnant social inequality and exclusion in the distribution of the opulent wealth garnered from oil in the region.
The fundamental human right is the right to life, which is not worth living without human dignity.
The way in which the right to life is being violated should arouse concern. According to various sources, more than 111 million people have perished in armed conflicts during modern wars. It cannot be forgotten in this room that, if in World War I civilian deaths amounted to 5 percent of total casualties, in the subsequent wars of conquest after 1990, basically in Iraq, with more than one million, and Afghanistan with more than 70,000, the deaths of innocents stand at 90 percent. The proportion of children in these figures is horrific and unprecedented.
The concept of ‘collateral damage’, an offense to human nature, has been accepted in the military doctrine of Nato and the very powerful nations.
In the last decade, humanitarian international law has been trampled, as is occurring on the US Guantánamo Naval Base, which usurps Cuban territory.
As a consequence of those wars, global refugee figures have increased by 34 percent, to more than 26 million people.
Military spending increased by 49 percent in the decade, to reach $1.5tr, more than half of that figure in the United States alone. The industrial-military complex continues producing wars.
Every year, 740,000 human beings die, not only on account of conflicts, but as victims of violent acts associated with organised crime.
In one European country, a woman dies every five days as a result of domestic violence. In the countries of the South, half a million mothers die in childbirth every year.
Every day, 29,000 children die of hunger and preventable diseases. In the minutes that I have been speaking, no less than 120 children have died. Four million perish in their first month of life. In total, 11 million children die every year.
There are 100,000 deaths a day from causes related to malnutrition, adding up to 35 million a year.
In Hurricane Katrina alone, in the most developed country in the world, 1,836 people died, almost all of them African Americans of few resources. In the last two years, 470,000 people died throughout the world as a result of natural disasters, 97 percent of them of low income.
In the January 2010 earthquake in Haiti alone, more than 250,000 people died, almost all of them resident in very poor homes. The same thing occurred with homes swept away by excessive rainfall in Rio de Janeiro and Sao Paulo in Brazil.
If the developing countries had infant and maternal mortality rates like those of Cuba, 8.4 million children and 500,000 mothers would be saved annually. In the cholera epidemic in Haiti, Cuban doctors are treating almost half of the patients, with a mortality rate five times lower than those being treated by physicians from other countries. Cuban international medical cooperation has made it possible to save more than 4.4 million lives in dozens of countries in four continents.
Human dignity is a human right. Today, 1.4 billion people are living in extreme poverty. There are 1.2 billion hungry people, and a further two billion are suffering from malnutrition. There are 759 million illiterate adults.
Mr President:
The Council has demonstrated its capacity for approaching human rights situations in the world, including those of an urgent nature which require attention and action on the part of the international community. The usefulness of the Universal Periodic Review, as a means of sustaining international cooperation, of evaluating the undertakings of all countries without distinction in this context has been confirmed.
The spirit which animated our actions during the review process of this body was to preserve, improve and strengthen this council in its function of effectively promoting and protecting all human rights for everyone.
The results of this exercise express a recognition of the Council’s important achievements in its short existence. While it is true that the agreements reached are insufficient in the light of the demands of developing countries, the body has been preserved from those whose aim was to reform it to their convenience in order to satisfy hegemonic appetites and to resuscitate the past of confrontation, double standards, selectivity and imposition.
It is to be hoped from the debates of the last few days that this human rights council will continue constructing and advancing its institutionalism toward the full exercise of its mandate.
It would be very negative if, on the pretext of reviewing the Council’s institutional construction and in abuse of the dramatic juncture which is being discussed, it should be manipulated and pressured in an opportunist way in order to establish precedents and modify agreements.
If the essential human right is the right to life, will the Council be ready to suspend the membership of states that unleash a war?
Is the Council proposing to make some substantial contribution to eliminating the principal threat to the life of the human species which is the existence of enormous arsenals of nuclear weapons, an infinitesimal part of which, or the explosion of 100 warheads, would provoke a nuclear winter, according to irrefutable scientific evidence?
Will it establish a thematic procedure on the impact of climate change in the exercise of human rights and proclaim the right to a healthy atmosphere?
Will it suspend states which finance and supply military aid utilised by recipient states for mass, flagrant and systematic violations of human rights and for attacks on the civilian population, like those taking place in Palestine?
Will it apply that measure against powerful countries which are perpetrating extra-judicial executions in the territory of other states with the use of high technology, such as smart bombs and drone aircraft?
What will happen to states which accept secret illegal prisons in their territories, facilitate the transit of secret flights with kidnapped persons aboard, or participate in acts of torture?
Can the Council adopt a declaration on the right of peoples to peace?
Will it adopt an action programme that includes concrete commitments guaranteeing the right to alimentation in a moment of food crisis, spiraling food prices and the utilisation of cereal crops to produce biofuels?
Mr President:
Distinguished ministers and delegates:
What measures will this Council adopt against a member state which is committing acts that are causing grave suffering and seriously endangering physical or mental integrity, such as the blockade of Cuba, typified as genocide in Article 2, Paragraphs B and C, of the 1948 Geneva Convention?
Thank you very much.
Translated by Granma International


